3D Printers
More opportunities through additive manufacturing technologies.
Additive manufacturing demonstrates its strengths where conventional manufacturing technologies reach their limits. Its key advantages are faster product development and procurement, improved product properties, and significant cost savings. The keys to these benefits are, on the one hand, the right application and, on the other hand, a shift in product development thinking. However, to unlock this potential, experience and knowledge about these technologies are necessary.
Benefit from our extensive industry expertise for your needs.
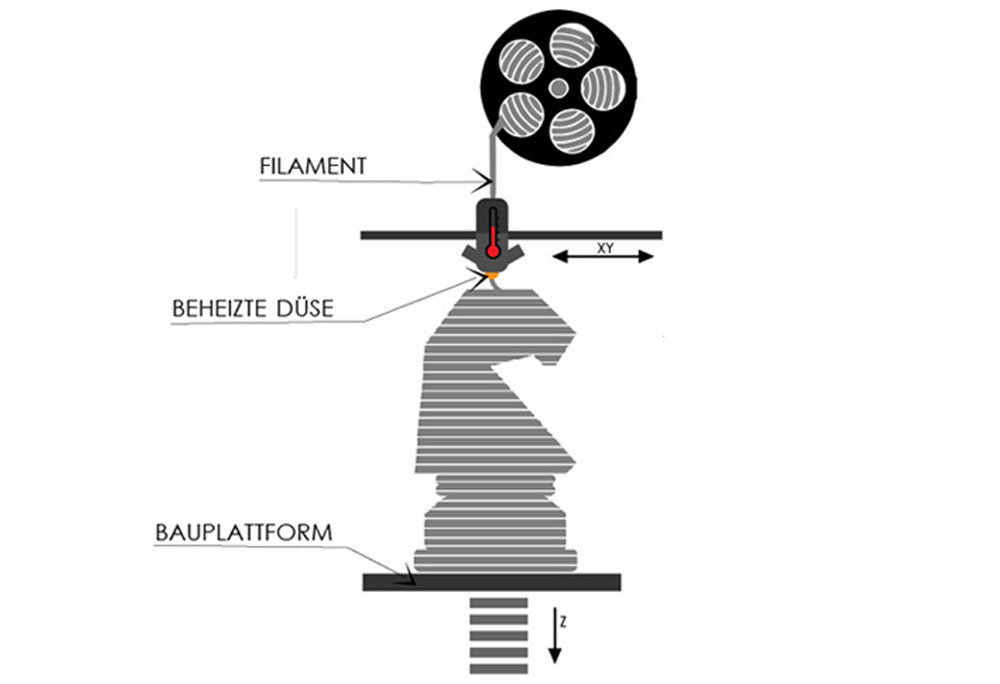
FFF
(Fused Filament Fabrication)
In the Fused Filament Fabrication process, a 3D object is built layer by layer from a thermoplastic material.
Applications
- Prototype development
- Small series production
- Mold making
- Functional parts
- Design & Architecture
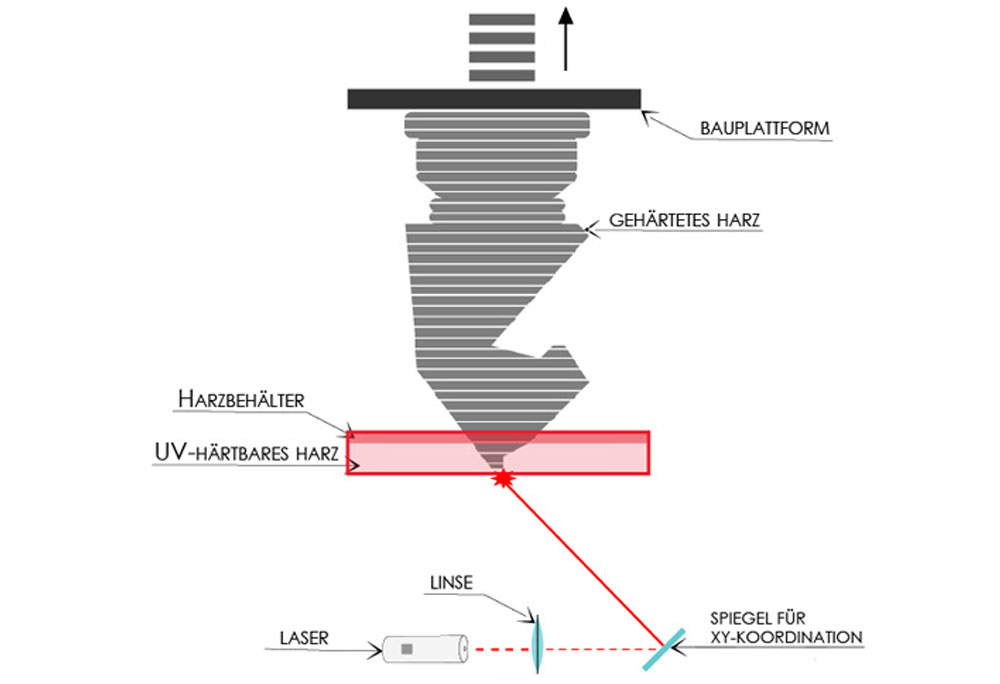
SLA
(Stereolithography)
In the stereolithography process, light-curing resins are cured layer by layer by a laser. These resins are called photopolymers.
Applications
- Audio industry
- Jewelry industry
- Dental industry
- Master models for vacuum casting
- Small series production
- Prototype construction
SLM
(Selective Laser Melting)
In Selective Laser Melting, the powder material is locally melted completely by laser radiation and applied in a thin layer on a base plate.
Applications
- Prototype manufacturing
- Small series production
- Mold making
- Functional parts
- Design & architecture
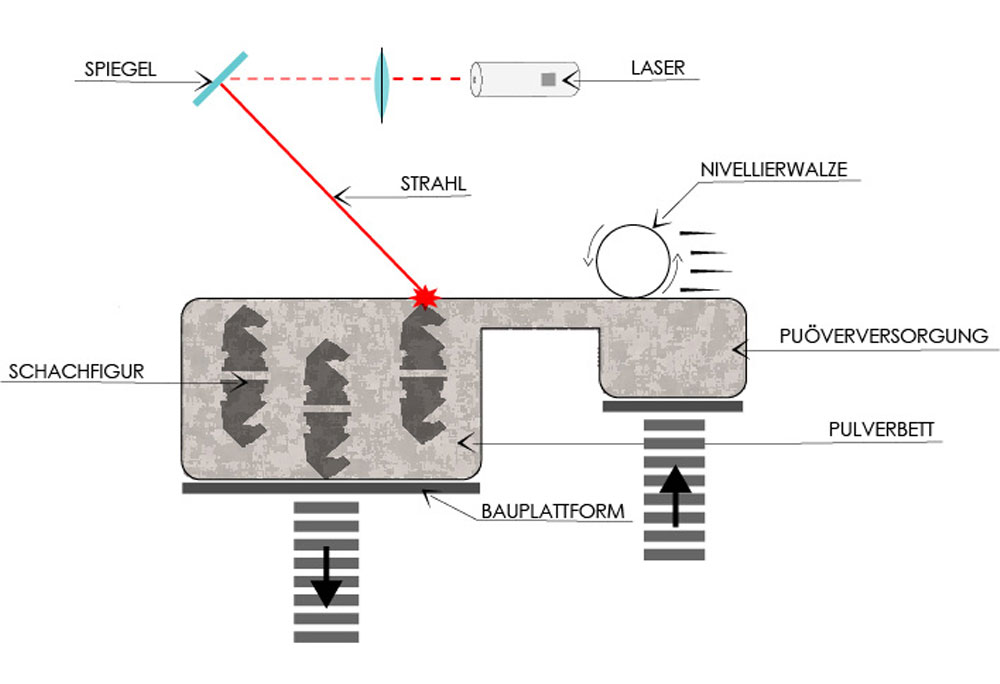
SLS
(Selective Laser Sintering)
Selective Laser Sintering is a process where powdered base material is fused layer by layer using a laser.
Applications
- Prototyping
- Small series production
- Mold making
- Functional parts
- Design & Architecture
Generative Technologies Compared
| FFF | SLA | SLS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oberflächenqualität | |||
| Detailgenauigkeit | |||
| Bauteilbelastung | |||
| Temperaturbeständigkeit | |||
| Ausgangsmaterial | Filament | Flüssigkeit | Pulver |
| UV-Beständigkeit | |||
| Geeignet für Prototyping |
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing is the process of creating real three-dimensional parts based on data sets. The model to be created is first developed as a 3D data set in any CAD program. With basic 3D printing experience, customized software, and material knowledge, this technology is accessible to everyone.
There are various methods for creating 3D prototypes, which are used in 3D printers.
FFF
(Fused Filament Fabrication)
One or more thin plastic filaments (usually PLA or ABS) are melted and applied layer by layer through nozzles at the desired locations. The material hardens there, creating a plastic part. As the part slowly hardens during the printing process, support material must also be built up by the printer. This support material is manually removed after the printing process and must then be disposed of. Post-processing of the parts can be more or less labor-intensive depending on the shape of the part. Simple, multi-colored models can be produced. The layers are typically slightly visible on the surface.
SLA
(Stereolithography)
This process uses liquid resin or wax as the starting material. A UV light source or a laser hardens the liquid material at the desired locations. This technology is particularly well-suited for creating vacuum casting master models. It allows for a very smooth and precise surface. Only single-color models can be produced.
SLS
(Selective Laser Sintering)
Here too, the base material is a very fine powder. Unlike powder printing, the material is not bonded by a binding agent, but rather fused using a laser beam. The quality and applications are comparable to those of powder printing. The components are somewhat more stable immediately after the printing process, making them easier to post-process. The models can only be printed in a single color.